Here's how to enable Safe Mode in Windows
Safe Mode lets you troubleshoot common problems with your PC.
 Credit:
Microsoft
Credit:
Microsoft
Products are chosen independently by our editors. Purchases made through our links may earn us a commission.
If your Windows 10 or 11 PC is having problems and you aren’t sure where to start troubleshooting, booting your computer into Safe Mode is a great place. Safe mode lets you pick apart problems in your computer without your usual programs taking up resources. It’s a versatile troubleshooting tool, and there are several ways to boot into it instead of your full operating system. You can boot into safe mode from your settings menu, your sign-in screen, or from a blank or black screen if you can’t even turn your computer on—here’s how.
What is Safe Mode?
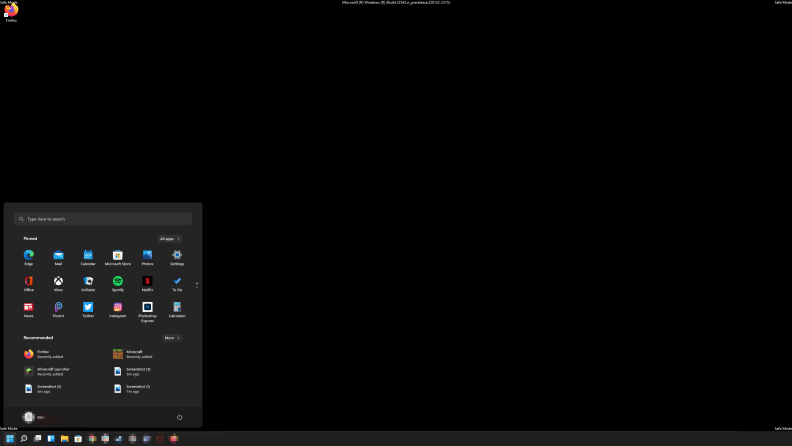
Safe Mode's simple laayout makes it easier to diagnose problems
Safe Mode is Windows’ diagnostic mode. When you boot into Safe Mode, the computer will only run the programs and drivers it needs for basic functionality. That means all of your startup apps, your network configuration, and even your video card’s driver will not boot on startup. That way, you can launch each driver or program as needed so you can identify the problem and troubleshoot accordingly without interference from other applications.
Using the settings menu

Windows 11's repair menu is rich and features a variety of tools.
This is the most straightforward method, but it requires you to boot into Windows normally.
Once you’re logged into your computer, access the settings menu by either pressing the Windows key + I or by clicking the start button and then clicking Settings. From here, select System and go to the Recovery submenu.


In WinRE, the advanced options give you tools to diagnose your PC at an instance.
In the Recovery menu, go to Advanced Setup and select Restart Now. This will restart your computer into the Windows Recovery Environment where you can use various troubleshooting tools. Click Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > Settings > Restart.
This will restart your computer with various boot options, including Safe Mode.
Using the sign-in screen

In the bottom right corner, the sign-in screen has a power button.
Sometimes, you can’t log into Windows or access the settings menu, and that’s okay. You can access Safe Mode from the Windows sign-in screen.
First, press the power icon, hold down the Shift key, and then press Restart from the power menu. This will restart your computer into the Windows Recovery Environment where you can use various troubleshooting tools. Click Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > Settings > Restart.
This will restart your computer to give you the option to reboot it in Safe Mode.
From a black or blank screen

When this (or a similar screen) appears, press the power button on an hold for ten seconds or more.
If you’re having trouble booting Windows, then this method is for you. You can do this by power cycling your device—completely shutting it down and turning it back on again—and then restarting your computer into safe mode from the Windows Recovery Environment.
First, while your PC is on, hold down the physical power button on your computer for ten seconds to turn it off. Press the power button again to turn it back on. As soon as the display shows any image (usually some basic text along with the logo of your motherboard manufacturer), hold the power button again for ten seconds.
Turn the PC back on, and like last time, hold the power button for ten seconds as soon as the display lights up to turn it off.
Turn your computer on one final time. Your computer should restart into something called Automatic Repair. Here, select Advanced Options to enter the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE).
In WinRE, click Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > Settings > Restart.
Now you can reboot in Safe Mode Safe Mode.
What if you still can’t enable Safe Mode?
If you have tried booting Windows into Safe Mode with any of the above options and you still can’t click Enable Safe Mode, press either 4 or F4 to access it. If you need network connectivity, press 5 or F5 to enable safe mode with networking.
How to leave safe mode

The run prompt lets you access features you may not find in menus.
Once you’re ready to start Windows normally, you should be able to just restart your computer directly from safe mode. If it does not boot into regular Windows, then you can manually disable safe mode with the Run prompt.
To access the Run prompt, press the Windows key + R. In the box, type msconfig, then press OK.

The highlighted check box should be unchecked to boot into windows normally.
Select the Boot tab in the new pop up. Go to Boot Options, and uncheck the Safe boot checkmark. Now restart your computer.
The product experts at Reviewed have all your shopping needs covered. Follow Reviewed on Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram for the latest deals, product reviews, and more.


